BACKGROUND
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is a complex health condition that occurs when the body does not receive the right balance of nutrients. It can result from a deficiency, due to insufficient intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and calories, or from an excess, where there is overconsumption of calories or specific nutrients. This imbalance can lead to various health issues, including stunted growth, wasting, micronutrient deficiencies, and even obesity. Malnutrition remains a major global health challenge, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations, particularly women and children in Africa and Asia. Despite progress in recent decades, the world is not on track to meet global targets for reducing malnutrition. This underscores the critical importance of measuring nutrition in all its forms to guide evidence-based policies, design effective interventions, and monitor progress. Robust measurement enables timely identification of at-risk populations and helps ensure coordinated efforts to improve nutrition and promote long-term health and well-being worldwide.

Quick Facts
Malnutrition remains a critical challenge, with millions of children suffering from severe wasting, stunting, and overweight. CHAMPS is addressing this huge burden in Africa and Asia by implementing innovative, data-driven strategies to improve nutrition in vulnerable communities, saving lives and creating a healthier future for children.

0 m+
people worldwide are undernourished.

0 m+
children under 5 affected by stunting

0 %
Malnutrition is the underlying cause of nearly half of deaths in children under five.

0 .5 trillion ($)
The global cost of malnutrition is estimated to be up to $3.5 trillion per year.
STUDY SITES
METHODS
How CHAMPS measures malnutrition
Postmortem anthropometry
Postmortem hemoglobin
Micronutrient biomarker testing of liver and serum to measure:
Liver Vitamin A

Liver iron/zinc

Inlammation
Serum vitamin A
Serum B12

Serum folate

Serum iron
Pregnancy Surveillance

Recent Data
| Total | BD(n=2922) | ET(n=3363) | KE(n=1733) | ML(n=1802) | MZ(n=2838) | NG-B(n=46) | NG-CR(n=254) | PK(n=668) | SL(n=1826) | ZA(n=1743) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight | 6093 | 932 | 1039 | 851 | 470 | 845 | 17 | 96 | 95 | 702 | 1046 |
| Stunting | 5095 | 784 | 928 | 597 | 384 | 934 | 19 | 69 | 90 | 466 | 824 |
| Wasting | 2971 | 293 | 394 | 639 | 245 | 294 | 4 | 68 | 42 | 560 | 431 |
| Any malnutrition | 7602 | 1048 | 1264 | 1082 | 576 | 1172 | 22 | 133 | 120 | 906 | 1278 |
| Category | Total | BD | ET | KE | NG-B | NG-CR | ML | MZ | SL | ZA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stillbirth/Death in first 24 hours (n=5123) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Neonates (n=2311) | 12 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Infant/Child (n=2421) | 606 | 6 | 124 | 169 | 0 | 2 | 56 | 56 | 150 | 30 |
| Total (n=9855) | 618 | 6 | 128 | 170 | 0 | 2 | 58 | 60 | 151 | 30 |
Figure. Burden of anemia and severe anemia in deaths 0-59 months
Indicator
Figure. Widespread vitamin A deficiency based on gold-standard liver retinol with concerns of age-specific vitamin A excess or toxicity in certain countries (n=320) (Deficient ≤0.1 μmol/g, Adequate >0.1 to <0.7 μmol/g, High ≥0.7 to <1.0, hypervitaminosis ≥1.0) (preliminary results). Similar results published in Gupta et al., 2024.
Reference
Figure. Prevalence of anemia by trimester in CHAMPS pregnancy surveillance in Ethiopia and Kenya (using venous blood measured by HemoCue201+; adjusted for altitude per WHO guidance and using trimester-specific cutoffs) (preliminary results)
Figure. Malnutrition (based on postmortem anthropometry) contributes to 40% of under-5 deaths and is associated with a 2.4-fold higher risk of infectious mortality
Reference
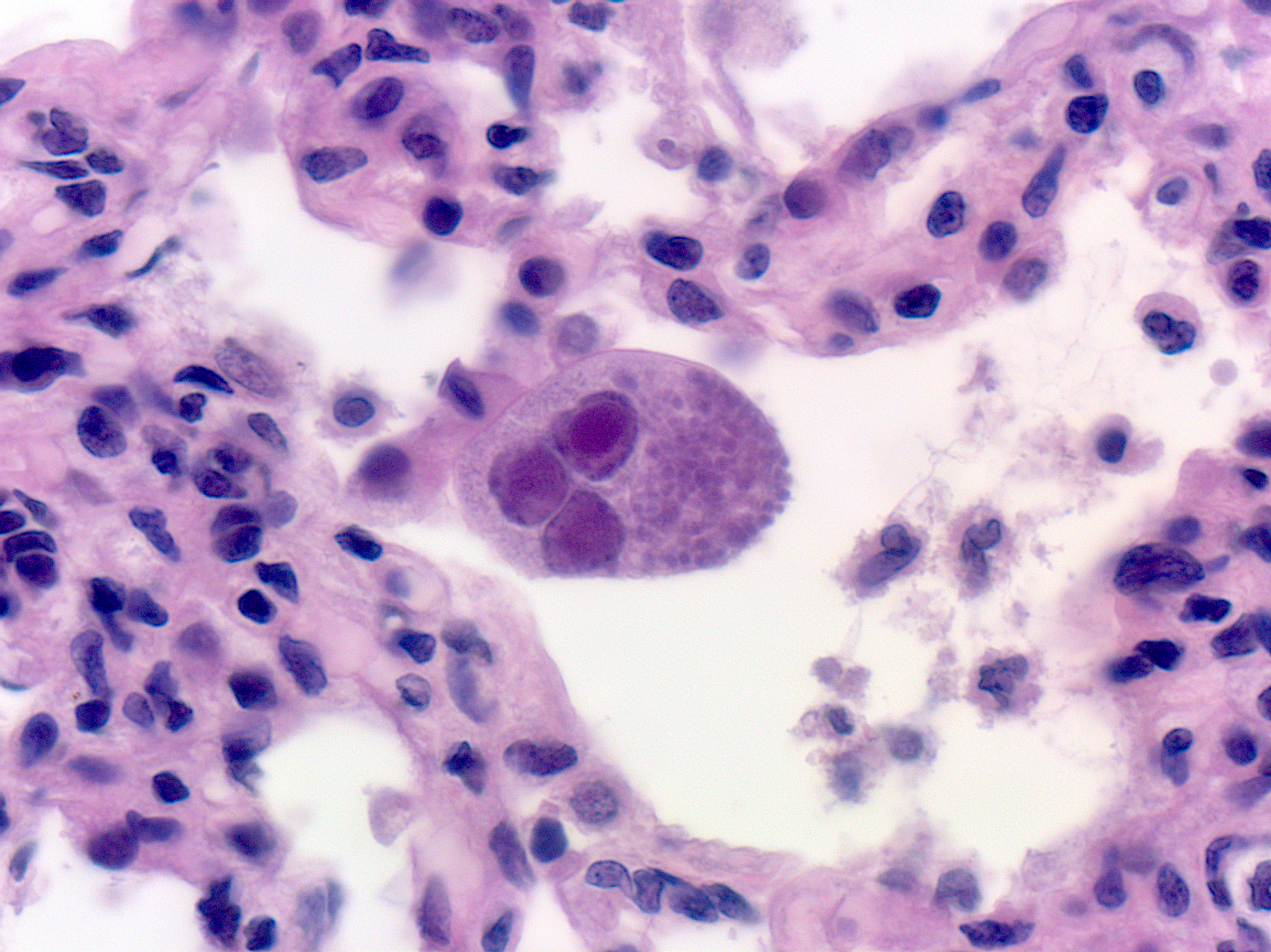
Figure. Alarming high rates of neural tube defects in Ethiopia, linked to widespread folate deficiency
Reference
Case Examples
Case Studies
Minimally Invasive Tissue Sampling in Adult Populations
View CHAMPS summarized child mortality data, updated in real time, and request access to our datasets.